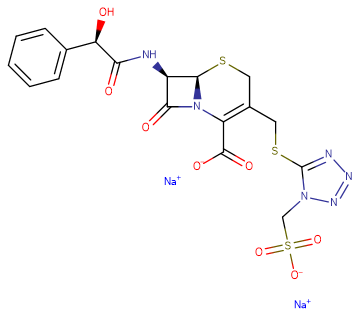
Cefonicid sodium
CAS No. 61270-78-8
Cefonicid sodium( Monocid )
Catalog No. M15306 CAS No. 61270-78-8
Cefonicid sodium is a broadspectrum cephalosporin antibiotic which inhibits the formation of the bacterial cell wall.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 25MG | 34 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | 50 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | 70 | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | 104 | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameCefonicid sodium
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionCefonicid sodium is a broadspectrum cephalosporin antibiotic which inhibits the formation of the bacterial cell wall.
-
DescriptionCefonicid sodium is a broadspectrum cephalosporin antibiotic which inhibits the formation of the bacterial cell wall.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
SynonymsMonocid
-
PathwayGPCR/G Protein
-
TargetAntibacterial
-
RecptorPBPs
-
Research AreaInfection
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number61270-78-8
-
Formula Weight586.53
-
Molecular FormulaC18H16N6Na2O8S3
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityWater: 10 mM
-
SMILESC1C(=C(N2[C@H](S1)[C@@H](C2=O)NC(=O)[C@@H](C3=CC=CC=C3)O)C(=O)[O-])CSC4=NN=NN4CS(=O)(=O)[O-].[Na+].[Na+]
-
Chemical Namedisodium;(6R,7R)-7-[[(2R)-2-hydroxy-2-phenylacetyl]amino]-8-oxo-3-[[1-(sulfonatomethyl)tetrazol-5-yl]sulfanylmethyl]-5-thia-1-azabicyclo[4.2.0]oct-2-ene-2-carboxylate
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.Rake JB, et al. J Antibiot (Tokyo). 1984 May;37(5):572-6.
molnova catalog



related products
-
Demeclocycline
Demeclocycline (Declostatin) is a tetracycline antibiotic produced by a strain of Streptomyces aureofaciens.Demeclocycline has antimicrobial activity and inhibits the action of vasopressin on the renal tubules, leading to diuresis.
-
BEC HCl
BEC HCl is a competitive arginase inhibitor, which bind slowly. Ki of BEC HCl is 0.31 μM (pH7.5) for Arginase II, and is 0.4-0.6 μM for rat Arginase I.
-
Tildipirosin
Tildipirosin is a 16-membered macrolide used as an antibiotic in veterinary medicine. Like other macrolides it inhibits protein synthesis in bacteria and blocks the production of biofilms.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


